The pyramid food model is a visual guide that helps people understand how to eat a balanced and healthy diet each day. It shows how much of each food group should be eaten for good health. The food concept is widely used across the world, and it makes nutrition easier to understand. The main idea is to eat more foods from the bottom of the pyramid and fewer from the top. This way, people can get the energy and nutrients they need. By using this food as a guide, families can plan better meals and prevent diet-related diseases.

History of Pyramid Food
The first pyramid food model was introduced in Sweden in the 1970s and later adopted globally for public health. It became popular because of its simple design, which organized food into levels. The base represented the most important foods, and the top included foods to limit. Over the years, many countries created their own versions of the food. Each design reflects cultural food habits while keeping the same healthy eating principles. For example, rice may be more common in Asia compared to bread in Europe.
Structure of Pyramid Food
The food has four main levels, each showing a group of foods and their role in the diet. The base is the widest and shows what should be eaten the most. The top is the smallest and shows what should be limited. This clear design helps people make daily choices without confusion. By looking at the food, one can see how much of each group is recommended. This makes it easier for parents, children, and adults to plan meals together.
Base of Pyramid Food
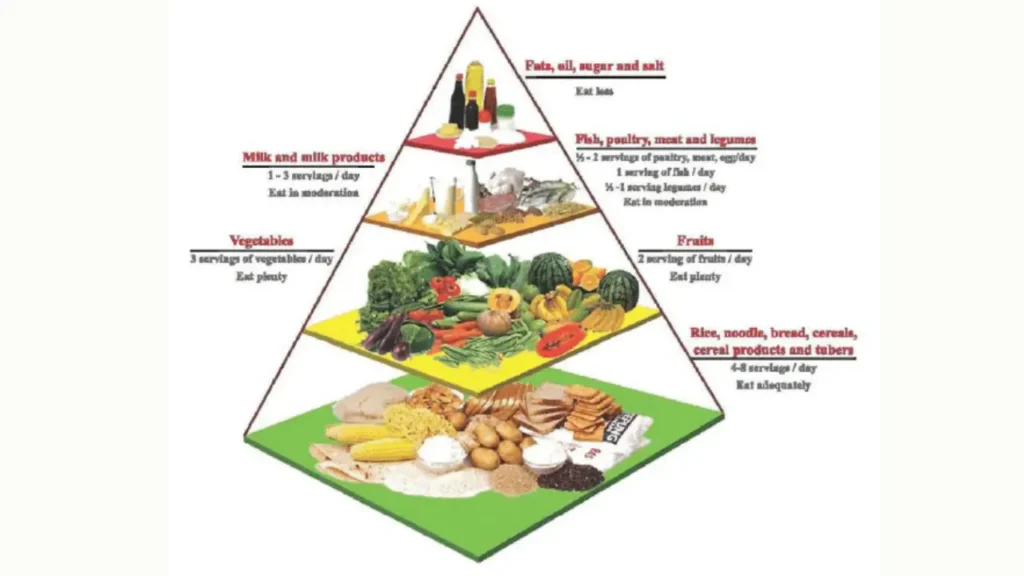
At the base of the pyramid are carbohydrates like rice, bread, cereals, pasta, and potatoes. These foods provide the main source of energy for the body. They should make up the largest part of daily meals because they fuel the brain and muscles. Whole grains are recommended at this level because they provide more fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Choosing brown rice or whole wheat bread is better for long-term health. The food encourages moderation even at the base, meaning not to overeat even healthy carbs.
Vegetables and Fruits
The second level of food includes vegetables and fruits. These are essential because they provide fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants. Eating a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables is important for a strong immune system. Nutrition experts recommend at least five servings of vegetables and fruits daily. The food shows them as a large section, highlighting their importance. Fresh, local, and seasonal produce is often healthier and more affordable.
Proteins
The third level of food includes protein-rich foods such as fish, eggs, poultry, nuts, and legumes. These foods help build and repair muscles, and they also support healthy blood and organs. Proteins should be eaten in moderate amounts to balance the diet. Fish is often recommended because it contains healthy fats that protect the heart. Legumes like beans and lentils are also great because they are affordable and rich in nutrients. The food encourages people to mix animal and plant proteins for better health.
Dairy and Calcium Sources
Dairy products like milk, yogurt, and cheese are also part of the third level of the pyramid. They are vital sources of calcium, which is important for strong bones and teeth. Children and teenagers especially need dairy to grow properly. People who cannot drink milk can choose alternatives like soy milk or fortified plant-based drinks. The food highlights the importance of these foods while reminding people not to overconsume high-fat dairy products. Balance is always the key.
Top of Food
The top of the pyramid is the smallest section and includes fats, oils, sweets, and salty snacks. These foods should be eaten rarely because they add extra calories without many nutrients. Examples include butter, fried foods, candy, and soft drinks. By keeping these foods at the top, the pyramid food teaches people to reduce sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats. This helps prevent obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. Choosing healthier oils and small portions of sweets is recommended.
Pyramid Food and Daily Portions
The food model also gives guidance on portion sizes for each group. Serving sizes help people avoid overeating and maintain balance. Different countries may adjust servings based on cultural diets, but the principles remain the same.
Here is a sample table showing daily recommended servings:
| Food Group | Servings per Day | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | 3–5 | Rice, bread, pasta, cereals |
| Vegetables | 3–4 | Spinach, carrots, broccoli |
| Fruits | 2–3 | Apples, bananas, oranges |
| Proteins | 2–3 | Fish, chicken, beans |
| Dairy | 2 | Milk, yogurt, cheese |
| Fats & Sweets | Small amounts | Butter, oils, candy |
This table shows how pyramid food gives practical steps for healthy eating each day.
Benefits of Following the Pyramid
Following the food helps reduce the risk of chronic diseases. It supports healthy weight, strong bones, and good heart health. It also encourages people to eat more natural foods instead of processed snacks. Another benefit is that it works for all ages, from children to adults. Families can follow the food together and enjoy healthier meals. Over time, this can save on medical costs and improve quality of life.
Modern Changes to the Pyramid
In recent years, some countries replaced the food with a plate model for easier use. For example, the U.S. uses the “MyPlate” method, showing half the plate as fruits and vegetables. However, the food is still widely used for teaching nutrition. Countries like Malaysia have updated their food to focus more on vegetables and water. These changes reflect growing health challenges like obesity and diabetes. The food continues to evolve while keeping its core message of balance.
Conclusion
The pyramid food model remains a simple but powerful tool for promoting healthy eating habits across the world. It teaches people to eat more whole grains, vegetables, and fruits while limiting fats, sugar, and salt. By following this guide, anyone can create a balanced diet that supports long-term health. The food may look simple, but it represents decades of research and cultural adjustments. Whether used in schools, homes, or communities, it continues to shape healthier lifestyles. Eating according to the food is not just a choice—it is a step toward a better and healthier future.